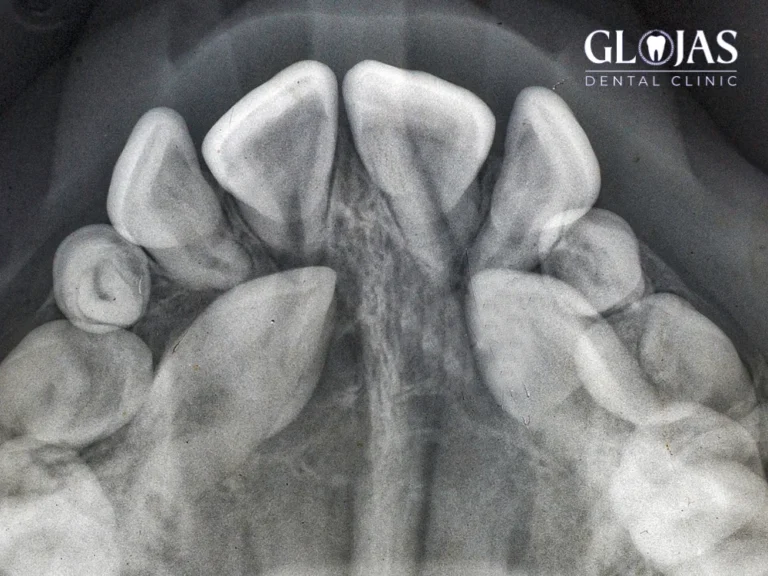
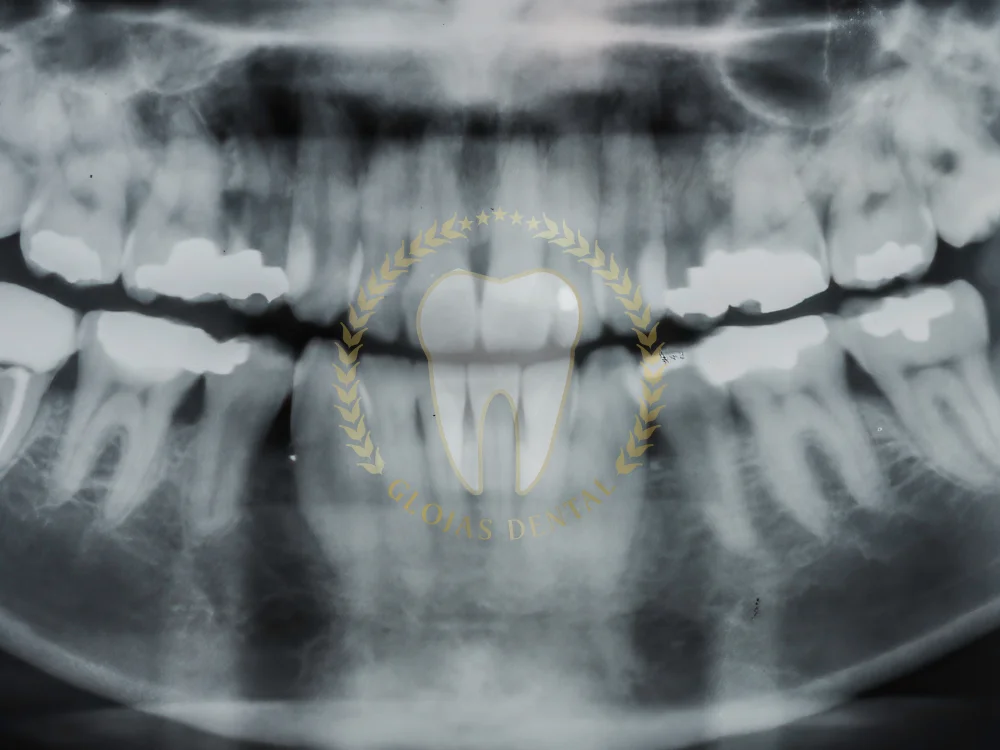
Impacted teeth can cause discomfort, dental alignment issues, and even long-term oral health complications. Canine impacted teeth, in particular, can pose significant challenges to oral health and aesthetics. These teeth play a crucial role in maintaining proper bite alignment and a balanced smile.
To address these issues and restore oral health, canine impacted tooth surgery may be necessary. This procedure involves surgically removing the impacted tooth or creating space for it to erupt properly. In this article, we will delve into the details of canine impacted tooth surgery, discussing the reasons for the procedure, the surgical process, and post-operative care.
What is a Canine Impacted Tooth?
The upper canine teeth, often referred to as cuspids or eyeteeth, are essential components of a healthy and functional smile. These teeth are responsible for tearing food, contributing to facial aesthetics, and maintaining proper alignment of the bite. However, in some cases, canine teeth may become impacted, meaning they fail to erupt through the gumline and remain embedded within the jawbone.
Impacted canine teeth can cause a range of dental issues, including crowding, misalignment, and potential damage to adjacent teeth. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for impacted canines is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health.
Why Do Canine Teeth Become Impacted?
Several factors contribute to canine teeth becoming impacted, including:
- Insufficient space: Crowding in the dental arch can prevent proper eruption.
- Abnormal positioning: Teeth growing at an incorrect angle may fail to surface.
- Genetics: A family history of dental anomalies often predisposes individuals to impacted teeth.
Why is Canine Impacted Tooth Surgery Necessary?
Delaying treatment for an impacted canine can lead to complications such as:
- Damage to adjacent teeth or roots
- Increased risk of cysts or infections
- Misalignment of other teeth
- Aesthetic concerns like gaps or irregularities in the smile
Undergoing canine impacted tooth surgery ensures that these issues are addressed proactively, improving both oral function and appearance.
The Steps of Canine Impacted Tooth Surgery
Understanding the surgical process can help ease anxiety and prepare you for the procedure. Here’s a breakdown of the typical steps:
1. Pre-Surgical Assessment
Before surgery, your dentist or oral surgeon will:
- Take X-rays or a 3D CT scan to locate the impacted tooth.
- Assess surrounding structures like nerves and sinuses.
- Discuss treatment plans and outcomes.
2. Anesthesia Administration
Most canine surgeries are performed under local or general anesthesia, ensuring a pain-free experience.
3. Creating an Incision
The surgeon will create a small incision in the gum tissue to expose the impacted canine.
4. Tooth Exposure or Extraction
Depending on the tooth’s position, it may be guided into place using orthodontic techniques or extracted if retention is not feasible.
5. Suturing the Area
The incision is closed with sutures, and follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor healing.
How to Prepare for Canine Impacted Tooth Surgery
Proper preparation ensures a smoother surgical experience:
- Follow dietary restrictions: Avoid eating or drinking for a specified time before surgery.
- Inform your surgeon of medications: Share any prescriptions or supplements you take.
- Arrange for post-surgery care: Have someone accompany you to and from the appointment.
Recovery After Canine Impacted Tooth Surgery
Post-operative care is critical to avoid complications and ensure speedy healing.
1. Managing Pain and Swelling
- Use prescribed pain medications or over-the-counter options like ibuprofen.
- Apply ice packs to reduce swelling during the first 24-48 hours.
2. Maintaining Oral Hygiene
- Avoid brushing near the surgical site for the first few days.
- Rinse gently with a saline solution or a dentist-recommended mouthwash.
3. Eating Soft Foods
Stick to soft, non-spicy foods like yogurt, mashed potatoes, and smoothies during the recovery period.
Orthodontic Considerations for Impacted Canines
In many cases, canine impacted tooth surgery is paired with orthodontic treatments. These include:
- Braces or aligners to create space for the tooth.
- Attachment placement: A bracket or chain may be attached to the tooth during surgery, facilitating its movement into place.
Combining surgical and orthodontic approaches ensures long-term success and prevents the recurrence of alignment issues.
Potential Risks of Canine Impacted Tooth Surgery
Like any surgical procedure, canine tooth surgery carries some risks:
- Infection at the surgical site
- Temporary numbness due to nerve involvement
- Sinus complications (rare, but possible with upper canines)
Discuss these risks with your oral surgeon and follow post-operative guidelines to mitigate potential issues.
Cost of Canine Impacted Tooth Surgery
The cost of surgery varies depending on factors like the complexity of the case, the surgeon’s expertise, and geographic location. On average, expect to pay between $500 and $2,500 per tooth. Orthodontic treatment adds to the overall expense.
Canine Impacted Tooth Surgery and Aesthetic Benefits
Beyond functional advantages, addressing impacted canines improves smile symmetry and facial aesthetics. Correct alignment can enhance your confidence and make daily interactions more enjoyable.
FAQs About Canine Impacted Tooth Surgery
1. What causes a canine tooth to become impacted?
Impacted canines often result from a lack of space in the dental arch, improper tooth angulation, or genetic predisposition.
2. Is canine impacted tooth surgery painful?
No, the procedure is performed under anesthesia to ensure a pain-free experience. Some discomfort may occur during recovery, which can be managed with medication.
3. How long does it take to recover from canine impacted tooth surgery?
Recovery typically takes 1-2 weeks, with complete healing occurring over several months. Following aftercare instructions is crucial for a smooth recovery.
4. Can an impacted canine be corrected without surgery?
In some cases, orthodontic treatments alone may guide an impacted canine into place. However, surgery is often required if the tooth is deeply embedded.
5. What are the signs of an impacted canine tooth?
Symptoms include swelling, pain, difficulty chewing, or noticeable gaps in the dental arch.
6. How can I prevent canine tooth impaction in my child?
Regular dental check-ups and early intervention with orthodontics can prevent or minimize the risk of canine impaction.
Conclusion
Canine impacted tooth surgery is a common dental procedure that can effectively address the issue of impacted teeth. By undergoing this procedure, you can prevent a range of dental complications, including pain, infection, and damage to adjacent teeth. It’s important to consult with a qualified oral surgeon to determine the best course of action for your specific situation. By addressing impacted teeth promptly, you can safeguard your oral health and enjoy a lifetime of healthy, beautiful smiles.