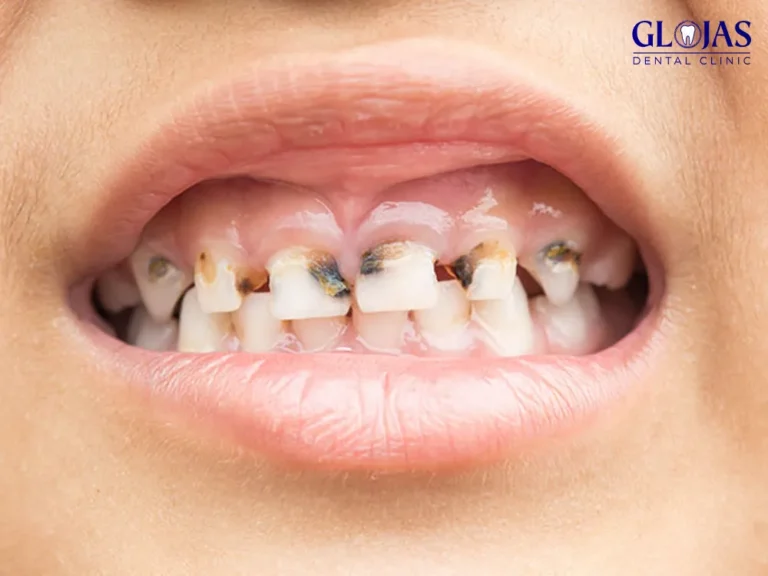
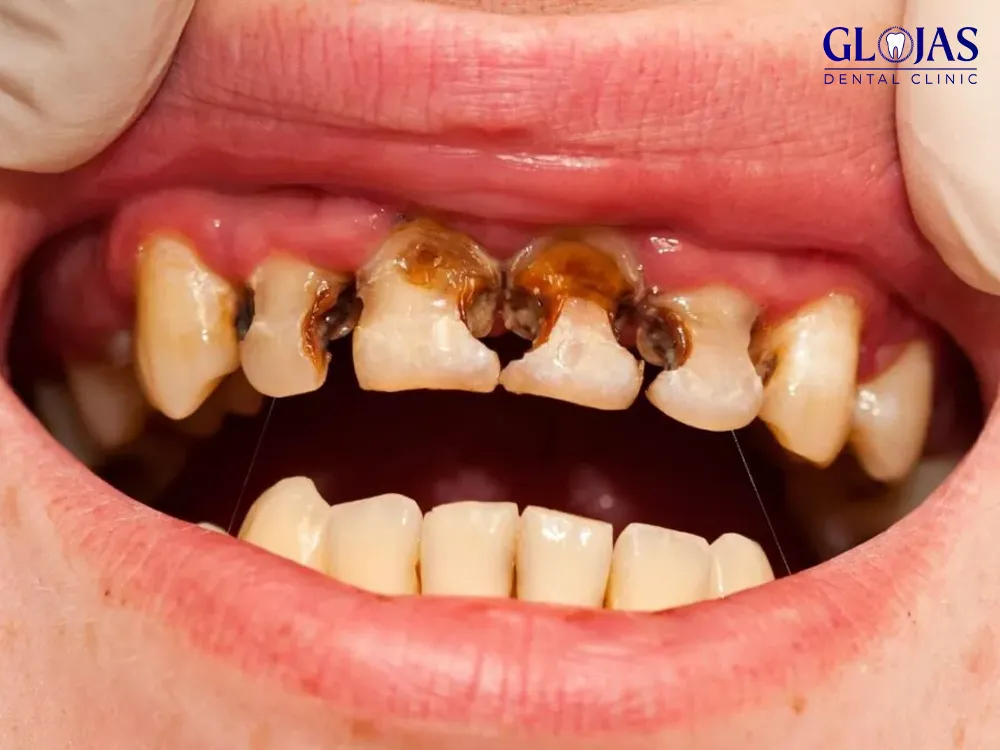
Tooth cavities, also known as dental caries, are among the most common oral health problems worldwide. They develop when the protective enamel of a tooth is eroded, leading to decay and potential damage to deeper layers. This guide will explore the causes, stages, and effective treatments for cavities, along with prevention tips to maintain a healthy smile.
Causes of Tooth Cavities

1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on the teeth, producing acids that erode enamel.
2. Sugary and Acidic Foods
Frequent consumption of sugary or acidic foods and beverages promotes bacterial growth, accelerating enamel erosion.
3. Dry Mouth
A lack of saliva reduces the mouth’s natural ability to wash away food particles and neutralize acids, increasing the risk of cavities.
4. Deep Pits and Grooves
Teeth with naturally deep grooves or pits are more prone to plaque accumulation, leading to decay if not cleaned effectively.
5. Frequent Snacking or Sipping
Constant snacking or sipping sugary drinks keeps teeth exposed to acids for extended periods, causing gradual enamel breakdown.
Stages of Tooth Cavity Development
Demineralization:
Early stage where enamel loses minerals due to acid attack. Appears as white spots on the tooth surface.
Enamel Decay:
The enamel breaks down, forming a small hole (cavity).
Dentin Decay:
Decay reaches the softer layer beneath enamel, causing sensitivity.
Pulp Damage:
The inner layer containing nerves and blood vessels is affected, leading to pain and possible infection.
Abscess Formation:
Severe infection can result in an abscess, requiring urgent treatment.
Treatments for Tooth Cavities
1. Fluoride Treatments
Best For: Early-stage cavities (demineralization).
Procedure: Application of fluoride gel, varnish, or foam to restore enamel.
Cost in Malaysia: RM50 – RM200 per session.
2. Dental Fillings
Best For: Cavities that have breached enamel but not reached the pulp.
Procedure: Decayed material is removed, and the cavity is filled with materials like amalgam, composite resin, or ceramic.
Cost in Malaysia: RM150 – RM450 per tooth.
3. Dental Crowns
Best For: Extensive decay weakening the tooth structure.
Procedure: The damaged portion is removed, and a custom-made crown is placed over the tooth.
Cost in Malaysia: RM800 – RM2,000 per crown.
4. Root Canal Treatment
Best For: Cavities reaching the pulp, causing pain or infection.
Procedure: The infected pulp is removed, and the tooth is sealed and crowned.
Cost in Malaysia: RM800 – RM2,500 per tooth.
5. Tooth Extraction
Best For: Severely decayed teeth that cannot be saved.
Procedure: The tooth is removed, and replacement options like implants or bridges are discussed.
Cost in Malaysia: RM150 – RM500 per tooth.
Prevention Tips for Tooth Cavities
Brush and Floss Regularly:
Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque.
Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks:
Reduce consumption of sugar-laden snacks and acidic beverages.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water to encourage saliva production and rinse away food particles.
Use Dental Sealants:
Protective coatings can be applied to the chewing surfaces of molars to prevent decay.
Regular Dental Checkups:
Visit the dentist every 6 months for cleanings and early detection of potential problems.
FAQs About Tooth Cavities
1. Can cavities heal on their own?
Early-stage cavities (demineralization) can be reversed with fluoride treatments, but advanced cavities require professional intervention.
2. Are cavities always painful?
Not necessarily. Cavities may not cause pain until they reach the dentin or pulp layers.
3. How long does a filling last?
The lifespan depends on the material: amalgam (10-15 years), composite (5-10 years), and ceramic (15+ years).
4. Can I prevent cavities without visiting a dentist?
While good oral hygiene helps, regular dental checkups are crucial for early detection and prevention.
5. Is it possible to get a cavity under a filling?
Yes, if the filling wears down or the seal breaks, bacteria can penetrate and cause decay underneath.
Conclusion
Tooth cavities are preventable and treatable with the right care and professional intervention. By understanding the causes, stages, and treatments available, you can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy, cavity-free smile. Regular dental visits, combined with good oral hygiene and lifestyle choices, are the key to long-term oral health.